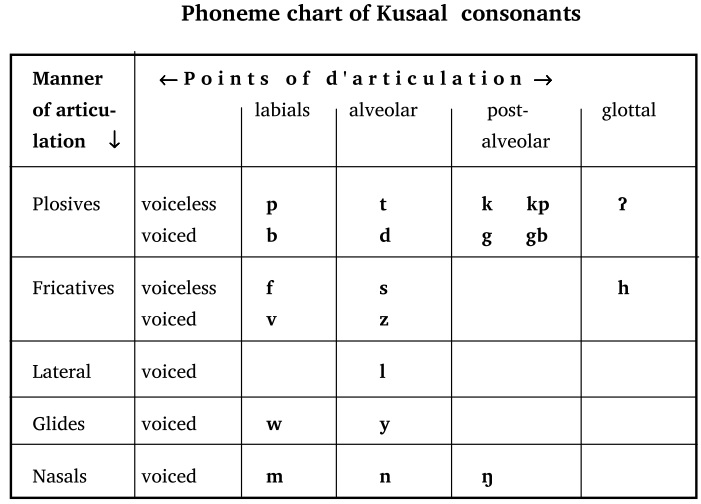
Phonology
For a Kusaal phonology description see the following PDF file «The Structure of Burkina Faso Kusaal» at https://www.kassena-ninkarse.org/burkina-faso/livres-langue-kusaal.html
or on https://www.kusaal-bf.com.
Phonemic vowel chart
| Short | Long | |||||
| Front
oral / nasal |
Central
oral / nasal |
Back
oral / nasal |
Front
oral / nasal |
Central or. / nas. | Back
or./ nas. |
|
| High close | i | u | i: | u: | ||
| High open | ɩ ɩ̃ | ʋ ʋ̃ | ɩ: ɩ̃: | ʋ: ʋ̃: | ||
| Mid close | e | o | e: | o: | ||
| Mid open | ɛ ɛ̃ | ɔ ɔ̃ | ɛ: ɛ̃: | ɔ: ɔ̃: | ||
| Low | a ã | a: ã: | ||||
The tonal system of Kusaal has three tones, high (H) and mid (M), and low (L) (which actually is phonetically a falling tone) as well as a down-stepped high tone (!H), symbolized by acute accent (á), middle accent (ā), grave accent (à), and for the down-stepped high tone a small elevated exclamation mark before acute accent (ꜝá).
High bã́ŋ H ‘bangle’
Mid bã̄ŋ M ‘crocodile’
Low õ̀ bã̀ŋ L ‘he knows’
High-Down-stepped kpã́'ʋ́ŋ H-ꜝH ‘guinea fowl’
Downdrift: The pitch is phonetically lowered at every transition from L to H. Pitch lowering can progress to a point that a H tone relatively late in the utterance has a lower pitch than an earlier L tone.
Stress is on the penultimate syllable.